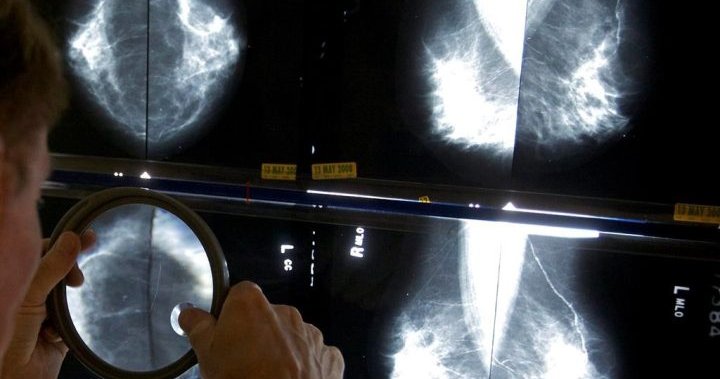
A recent early-stage study published in The Lancet Oncology has demonstrated that artificial intelligence (AI) can be a valuable tool in breast cancer detection, effectively improving the accuracy of diagnoses. The AI technology used in the study was able to reduce the workload of doctors reading mammograms by an impressive 44.3%. It is important to note that this study does not advocate for AI to replace radiologists, but rather to enhance their ability to read screens more quickly and accurately in a safe manner. While other studies have also shown promising results in utilizing AI for mammography screening, this study is unique as it is the first randomized trial to assign participants to experimental and control groups.
The researchers involved in this study conducted screenings of over 80,000 women between the ages of 40 and 80 at four sites in Sweden, from April 2021 to July 2022. The women were divided into two groups: the intervention group, where radiologists read mammograms with the assistance of AI, and the control group, where mammograms were read by two radiologists without AI support. The results showed that the intervention group had a cancer detection rate of 6.1 per 1,000 screenings, resulting in 244 detected cases out of a total of 39,996 screenings. In comparison, the control group had a detection rate of 5.1 per 1,000 screenings, with 203 detected cases out of a total of 40,024 screenings. Despite the increased cancer detection rate in the intervention group, both groups had a low false positive rate of 1.5%, indicating that the additional cancer detections made by AI were not due to over-sensitivity.
The use of AI in healthcare and research has been rapidly advancing, with promising outcomes. A previous study published in the journal Nature showed that AI can more accurately predict breast cancer than humans. The AI used in that study reduced false positives by 5.7% in U.S. datasets and 1.2% in U.K. datasets, and reduced false negatives by 9.4% in U.S. datasets and 2.7% in U.K. datasets, indicating its ability to identify cancers that may have been missed by human observers.
Breast cancer is the second leading cause of cancer-related deaths among Canadian women, making the advancements in AI-supported breast cancer detection particularly crucial. It is estimated that one in eight Canadian women will develop breast cancer during her lifetime, and unfortunately, one in 34 will succumb to the disease. To improve treatment options, researchers at a lab in Waterloo, Ontario have developed AI-driven technology that utilizes synthetic correlated diffusion MRI to capture detailed information about cancer tumors. This technology could greatly assist oncologists and medical doctors in personalizing treatment plans for breast cancer patients.
In conclusion, the study conducted in Sweden highlights the significant potential of AI in breast cancer detection by enhancing the accuracy and efficiency of mammogram readings. While AI should not replace radiologists, its integration into the screening process can lead to improved outcomes for patients. Additionally, AI advancements in healthcare, such as the development of AI-driven technology for personalized treatment plans, hold great promise for improving the overall management of breast cancer.
Denial of responsibility! VigourTimes is an automatic aggregator of Global media. In each content, the hyperlink to the primary source is specified. All trademarks belong to their rightful owners, and all materials to their authors. For any complaint, please reach us at – [email protected]. We will take necessary action within 24 hours.